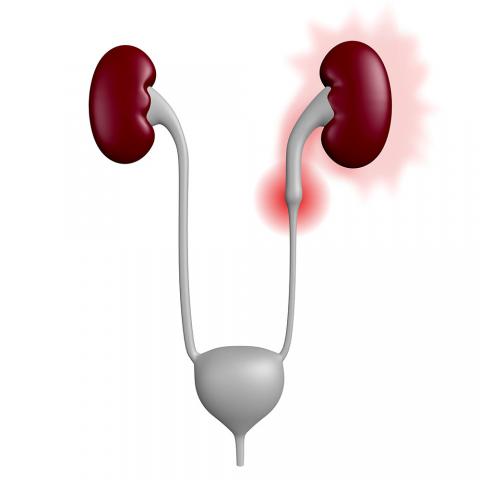
A stone within the ureter usually causes pain called renal colic. These stones always form within the kidney and while they are in the kidney, they frequently cause no symptoms. When a stone falls out of the kidney into the ureter, it often causes a blockage in the ureter and the backpressure of urine to the kidney causes severe pain.
The ureters are narrow tubes which transfer the urine made in the kidneys to the bladder. Very small stones, usually 1-2 mm, may pass through the ureter into the bladder without causing pain at all.
Stones which are 3mm or larger usually cause an obstruction to the ureter resulting in renal colic.
Stones which are up to 5mm usually can pass spontaneously without the need for surgical intervention, although they will frequently cause symptoms on their way out.
Calculi that are larger than 5 mm are unlikely to pass spontaneously and more often require intervention to extract the stone.